Cloves Benefits: Health Advantages, Nutrition, and Practical Uses in 2025
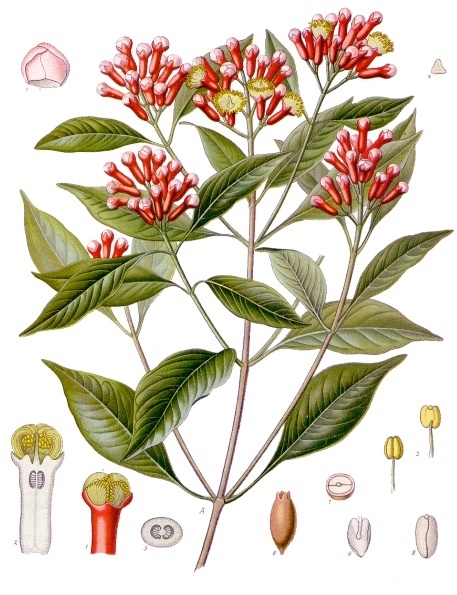
Cloves, derived from the flower buds of the Syzygium aromaticum tree, extend beyond their role as a seasonal spice. With a rich history in global trade and traditional medicine, cloves are now spotlighted in 2025 research for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties. This guide explores their historical significance, chemical makeup, evidence-based health benefits, and everyday applications to enhance wellness.
The Historical Significance of Cloves
Originating from Indonesia's Maluku Islands, cloves have influenced empires and trade routes for centuries. Ancient Chinese practices involved chewing cloves for fresh breath, while Arab traders transported them across vast distances. European powers sought control over clove production, underscoring their value in traditional systems like Chinese medicine for warming the body and Ayurveda for balancing doshas. Modern studies in 2025 continue to affirm these uses, linking cloves to neuroprotective and antimicrobial effects.
For more on spice histories, visit our Elite Blog.
Chemical Composition: Key Compounds in Cloves
Cloves' efficacy stems from their bioactive compounds:
- Eugenol: Comprising 70-90% of clove oil, it offers analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial benefits by interacting with pain receptors and inhibiting pathogens.
- Antioxidants: High ORAC values indicate strong protection against oxidative stress.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Includes vitamin C, K, A, E, manganese, magnesium, potassium, and iron.
- Fiber: Aids digestive health.
A 2025 study highlights cloves' role as natural preservatives due to these compounds.
| Nutrient (per 1 tsp/2g ground cloves) | Amount | % Daily Value* |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 6 | <1% |
| Manganese | 1.26mg | 55% |
| Vitamin K | 3mcg | 4% |
| Fiber | 0.7g | 3% |
| Vitamin C | 0.2mg | <1% |
*Based on a 2,000-calorie diet. Source: Recent nutritional analyses.
Science-Backed Health Benefits of Cloves
2025 research reinforces cloves' therapeutic potential:
- Antioxidant Protection: Combats oxidative stress, reducing risks for cardiovascular disease, cognitive decline, and cancer.
- Pain Relief: Eugenol provides relief for toothaches, muscle pain, and headaches.
- Digestive Health: Stimulates enzymes, prevents ulcers, and reduces bloating.
- Immune Boost: Antimicrobial properties fight infections and support respiratory health.
- Blood Sugar Control: Enhances insulin sensitivity and slows glucose absorption.
- Anti-Inflammatory: Lowers inflammatory markers, aiding chronic disease management.
Emerging Research on Cloves
- Cancer Prevention: Eugenol induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in lab studies.
- Liver Protection: Shields against toxins and fatty liver.
- Bone Health: Improves density and calcium absorption.
- Neuroprotection: Potential for managing neurological issues.
- Heart Health: Lowers cholesterol and supports cardiovascular function.
Human trials are ongoing to validate these findings.
Practical Ways to Incorporate Cloves
- Culinary Uses: Add to stews, rice, or baked goods; brew in teas or lattes.
- Remedies: Steep for digestive tea; dilute oil for topical pain relief.
- Aromatherapy: Diffuse for stress reduction.
Start with 1-2 grams daily in food.
Safety Considerations and Precautions
Cloves are generally safe in culinary amounts, but:
- Dilute essential oil to avoid irritation.
- Avoid high doses during pregnancy or in children.
- Consult a doctor if on blood thinners or diabetes meds, as interactions may occur.
Future Directions in Clove Research
2025 studies explore neuroprotective effects, weight management, skin applications, and cardiovascular benefits.
Conclusion
Cloves offer a versatile, natural boost to health, supported by historical use and modern science. Integrate them mindfully for optimal benefits.
Disclaimer: This information is educational; consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I consume cloves daily? Yes, in moderation (1-2g); monitor for sensitivities.
- Is clove oil safe for skin? Dilute properly to prevent irritation.
- Do cloves help with toothaches? Yes, via eugenol's anesthetic properties.
- Are cloves beneficial for weight loss? They support metabolism as part of a balanced routine.
- Safe for pregnancy? Culinary yes; avoid supplements without advice.
- Medication interactions? Possible with anticoagulants; seek medical guidance.
Share your clove experiences in the comments!
Related Articles on Elite Blog:



Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks for your response,May God bless you